Dec . 09, 2024 14:59 Back to list
drainage and sewage pump factory
The Evolution and Importance of Drainage and Sewage Pump Factories
In our modern society, effective drainage and sewage management is vital for public health, environmental protection, and urban development. The factories dedicated to manufacturing drainage and sewage pumps play a pivotal role in this sector, ensuring that we can manage waste and stormwater efficiently. This article explores the evolution of these factories, their significance, and the technology involved in modern pumping solutions.
Historically, the management of wastewater can be traced back to ancient civilizations. The Romans, for instance, developed complex sewer systems that included the use of rudimentary pump systems to manage water flow. However, it wasn't until the Industrial Revolution that the need for more sophisticated pumping solutions became apparent. This period marked the inception of dedicated factories focused on building pumps capable of handling larger volumes of waste and stormwater.
The Evolution and Importance of Drainage and Sewage Pump Factories
Modern sewage and drainage pumps can be categorized into several types, each designed for specific applications. Submersible pumps, for instance, are designed to operate while submerged in liquids, making them ideal for applications in sewage basins or flooded areas. Conversely, centrifugal pumps, widely used in municipal settings, function by converting rotational energy into the kinetic energy of liquid, efficiently moving large quantities of water and sewage.
drainage and sewage pump factory
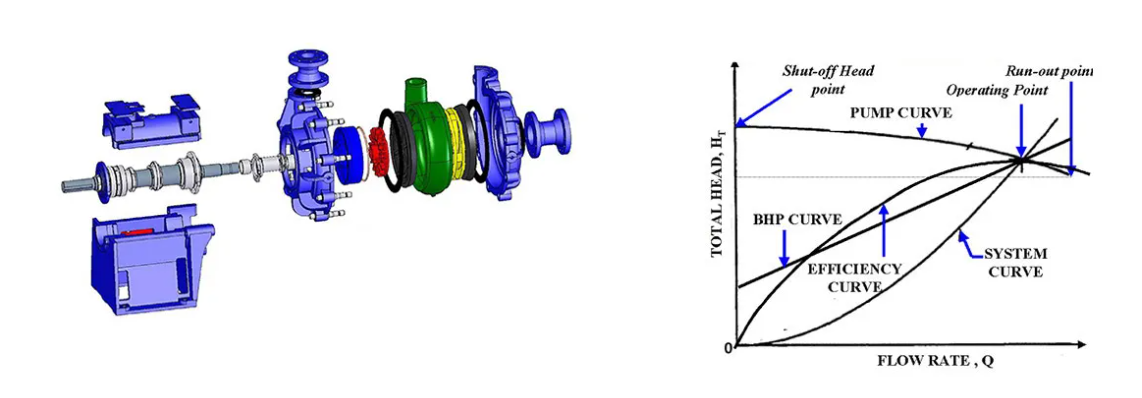
The importance of drainage and sewage pump factories cannot be overstated. They serve not only as manufacturers but also as innovators in the field of wastewater management. By continually researching and developing new technologies, these factories contribute to the creation of more efficient systems that reduce energy consumption and improve overall performance. For instance, the integration of smart technology into sewage pump systems has revolutionized operations, allowing for remote monitoring and automated adjustments based on flow conditions. This innovation significantly reduces manpower needs and enhances the reliability of pumping systems.
Furthermore, the environmental impact of sewage and drainage pumps is a growing concern. Factories are increasingly adopting sustainable practices in their manufacturing processes. This includes using recyclable materials, minimizing waste, and optimizing energy use in production. Additionally, the pumps themselves are designed to be more energy-efficient, reducing the carbon footprint of wastewater treatment facilities.
The global demand for advanced drainage and sewage solutions has led to an increase in specialized factories around the world. Countries facing rapid urbanization particularly benefit from these innovations. Cities that expand without adequate wastewater management infrastructure often experience flooding, pollution, and public health crises. The role of sewage and drainage pump factories is crucial in addressing these challenges by providing municipalities with the tools necessary for effective waste management.
Moreover, as climate change continues to impact weather patterns, the capability to handle increased stormwater is becoming essential. Factories are now focusing on flood control pumps designed to handle excessive rainfalls, helping cities mitigate flooding risks. This proactive approach demonstrates the adaptability of sewage and drainage pump manufacturers in responding to emerging environmental challenges.
In conclusion, drainage and sewage pump factories are integral to modern infrastructure, playing a critical role in managing wastewater and protecting public health. Through continuous innovation, sustainable practices, and an emphasis on efficiency, these factories are not only meeting current demands but also preparing for future challenges. As urbanization accelerates and climate change presents new risks, the significance of reliable drainage and sewage systems—and the factories that produce them—will only continue to grow. Their contributions are fundamental to ensuring a safer, cleaner, and more sustainable environment for generations to come.
-
High Quality Slurry Pump Seals Reliable China Suppliers & Manufacturers
NewsJun.24,2025
-
High Quality Portable Submersible Slurry Pump Supplier & Manufacturer from China
NewsJun.10,2025
-
Slurry Pump Parts Manufacturer – High Quality Rubber Spare Parts from China
NewsJun.10,2025
-
High Quality 1/3 HP Submersible Sump Pump with Vertical - Reliable Supplier & Factory Price
NewsJun.10,2025
-
High-Efficiency Centrifugal Slurry Pumps India
NewsJun.10,2025
-
High Quality Warman Centrifugal Slurry Pump Suppliers & Factory
NewsJun.10,2025
